Energy costs
Electricity Costs
Electricity Bill Components
A standard electricity bill is made up of:
- wholesale costs for generating the electricity from power plants
- retail costs reflecting electricity retailers operating and marketing costs
- network costs for transporting the electricity from power plants to the household (transmission and distribution costs)
- environmental policy costs, such as the Renewable Energy Target
On average, a residential electricity bill comprises:
- wholesale electricity costs make up 34%
- retail costs and profit margins make up 16%
- network costs make up between 43%
- environmental costs make up between 6%.
The Grattan Institute found that household electricity price rises in Victoria over the past decade have been driven by network investment and retail margins rather than the (wholesale) cost of generating electricity (Grattan Institute 2017).
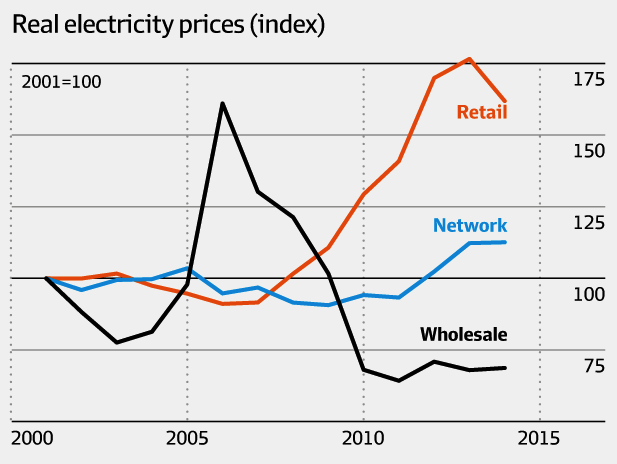
Image credit: Grattan Institute, 2017
Costs of New Power Generation
Australia needs a plan to replace ageing coal-fired power stations and to reduce pollution from the electricity sector; this will require investment in new low or zero pollution power plants, such as wind and solar. Wind and solar power are among the lowest cost sources of new power generation (Reputex and Carbon 2017).

Table: Levelised cost of energy for different power technologies
(**) Recent wind contract prices as low as US$55/MWh
For more detail see:
- Climate Council Electricity Prices: Sorting Fact from Fiction
- Climate Council New wind and solar now as cheap as existing coal
- Climate Council Factsheet: 10 Basic Electricity Facts to Help You Navigate the Finkel Review
- Climate Council Australia’s Electricity Sector: Ageing, Inefficient and Unprepared
- Climate Council Powering a 21st Century Economy: Secure, Clean, Affordable Electricity
